
Chicken is a common ingredient on the dining table. It has a wide variety of types, including chicken breast, chicken leg meat, chicken inner muscles, chicken wings, etc. In addition to the different tastes of each part, there are also considerable differences in nutrition. Japanese nutritionist Kasumi Yanagi (ㄡぎかお) analyzed the nutritional differences and cooking points of different parts of chicken in "yoga".
Parts of chickenParts of chicken include: chicken chest, chicken legs, chicken inner muscles, chicken heart, chicken liver, chicken neck, chicken wings, chicken wing roots, chicken middle wings, chicken gizzards, chicken tails, chicken skin and many other kinds. Chicken contains protein that is often insufficient in modern diets, and is also lower in popularity and price compared to other meat types. Nutritional differences between different parts:
Chicken has differences in heat, protein and fat content depending on the site. In addition, the vitamins contained in each part are also different. The following lists the protein and fat comparisons (per 100 grams):
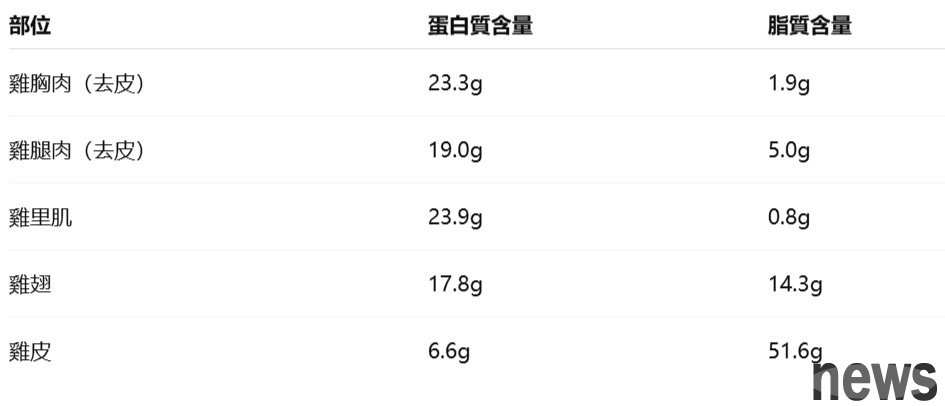
Chicken brisket
is only in Chicken Willow, with high protein content and low fat. It is one of the most affordable parts of chicken and a good choice for family protein supplementation. Contains rich in vitamin B1, tobacco acid, and the fatigue recovery ingredient "carnosine", which has attracted attention in recent years, this antioxidant amino acid helps muscle endurance.

Chicken leg meat
Protein content is second to inner muscles and breast meat. Although the fat is slightly higher, the meat is tender and resistant to cooking, which is suitable for various dishes. It contains vitamin B2, which protects mucosa, promotes healthy skin and hair, and is about twice as high as other parts, and is rich in vitamin K, which helps calcification and blood health.

Chicken muscle (chicken willow)
is the part with the highest protein content and the lowest fat content in chicken meat, and can be said to be the healthiest. Very suitable for weight loss and muscle building. The only disadvantage is that it is easy to dry after heating and the price is slightly higher.

Chicken wings
contain chicken skin, which is high in fat, but is also rich in gelatin. Although gelatin cannot be absorbed directly, consumption can promote the production of gelatin in the body. In recent years, studies have also pointed out that gelatin has the effect of strengthening blood vessels and is helpful for health and beauty.
Chicken skin
is extremely fatty, but it is also rich in gelatin, toxin acid and vitamin K that helps energy-relieving. Although tobacco acid is heat-resistant but water-soluble, it will be lost if boiled in water. It is recommended to be processed by baking, which can reduce fat intake.

It is recommended to eat soup juice together
The vitamin B group in chicken is water-soluble. If boiled in water or boiled, it will flow into the soup juice. It is recommended to choose a dish that can be eaten with soup and juice to completely store nutrients.
Add vinegar to increase the absorption rate of calcines
Chicken wings, chicken wing roots and other bone-facing parts. When boiling, the calcines in the bones will be revealed, but the absorption rate of human body to calcines is about 30%. Adding vinegar can increase the absorption rate to about two times.
Pretreatment to avoid drying areas with chicken breasts and chicken willows. Before cooking, you can soak the meat in cooking wine or salt water with a concentration of sea water for about 2 hours to allow the moisture to enter the muscle fiber. It is recommended to fry slowly over low heat when cooking. If boiling water, add heat after boiling water. Turn off the heat after boiling water and put a pot on the pot for about 10 minutes.